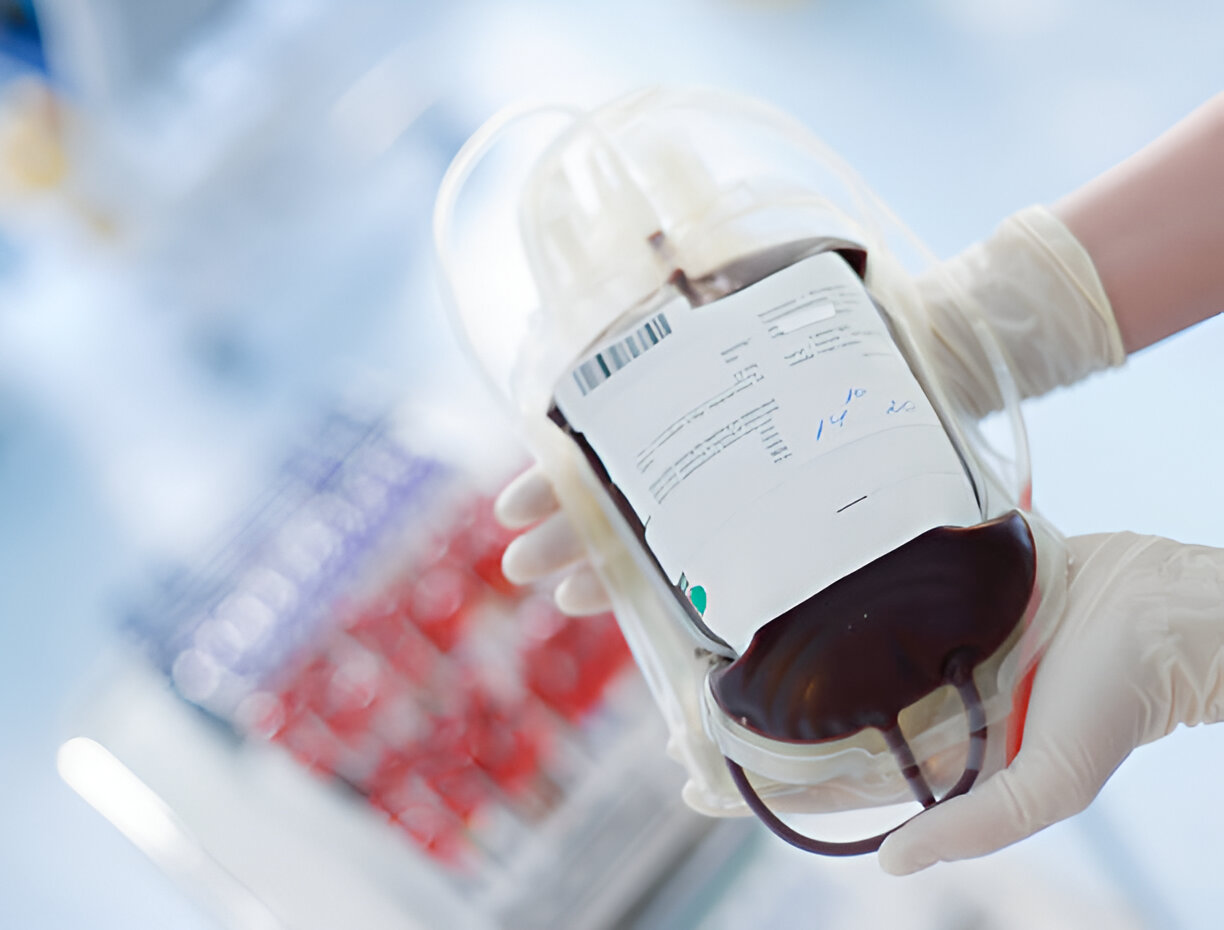
Blood bags are a critical component in the healthcare industry, designed for the collection, storage, transportation, and transfusion of blood and its components. These specialized medical devices are engineered to maintain the quality and safety of blood, ensuring that it can be used effectively to save lives in various clinical settings.
This article explores the types, uses, and importance of blood bags in modern medicine.
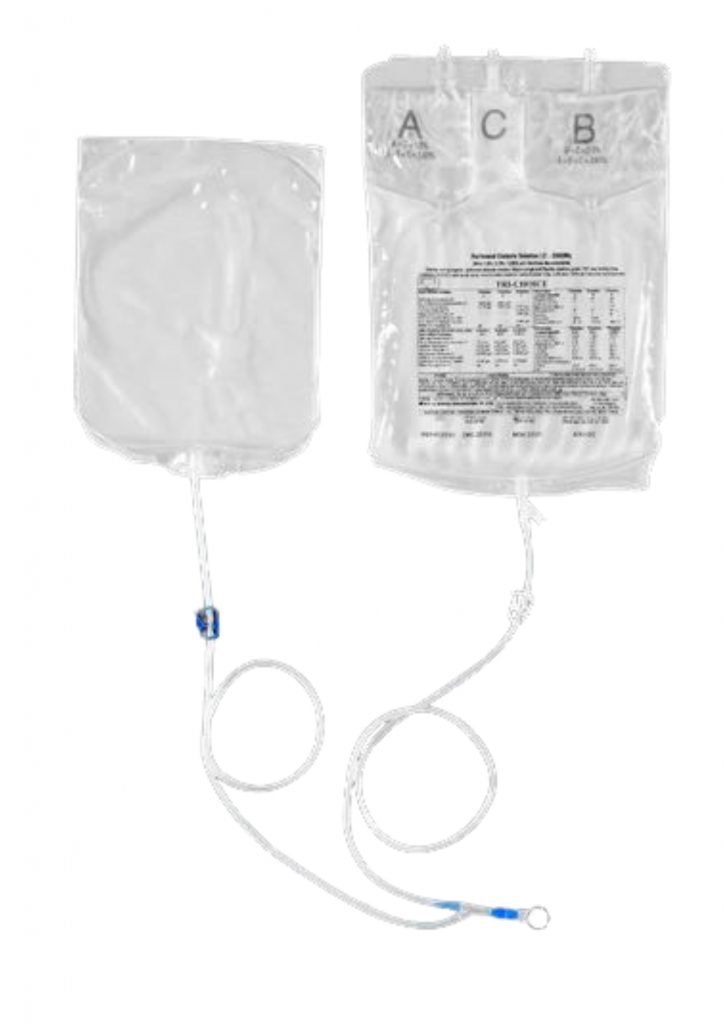
What Are Blood Bags?
Blood bags are sterile, medical-grade containers made of biocompatible plastic materials, typically polyvinyl chloride (PVC). They are specifically designed to safely handle blood and its components while preserving their biological properties. Blood bags are used in blood banks, hospitals, and healthcare facilities worldwide for transfusion and research purposes.
Types of Blood Bags
Blood bags come in various types to meet different clinical needs:
Single Blood Bags
Purpose: Used for the collection and storage of whole blood.
Components: These bags have a single compartment and are ideal for situations where no separation of blood components is needed.
Double Blood Bags
Purpose: Designed for the separation of whole blood into two components, typically red blood cells (RBCs) and plasma.
Components: Includes a primary bag for blood collection and a secondary bag for plasma or other components.
Triple Blood Bags
Purpose: Used to separate blood into three components: RBCs, plasma, and platelets.
Components: The main bag is connected to two satellite bags, making it possible to maximize the utility of each blood donation.
Quadruple Blood Bags
Purpose: Enables separation into four components: RBCs, plasma, platelets, and cryoprecipitate.
Components: Often used in advanced blood banking and transfusion medicine.
Apheresis Blood Bags
Purpose: Specifically designed for the apheresis process, where blood is collected, separated, and certain components are retained while the rest is returned to the donor.
Components: These bags are part of a more complex system used with apheresis machines.
Conclusion
Blood bags are indispensable tools in modern healthcare, ensuring the safe and efficient collection, storage, and utilization of blood. Their role in enabling life-saving transfusions and advancing medical research underscores their importance in clinical practice. Innovations in blood bag design and technology continue to improve the quality and safety of blood banking, benefiting patients and healthcare providers worldwide.